Diffusion Dynamics in Ecological Concrete Studied by Neutron Imaging Method
J. Zelenka, M. Dráb, S. Vratislav, L. Kalvoda, I. Medveď, V. Kočí, R. Černý, M. Kučeráková
Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering and Faculty of Civil Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague
Nowadays, most people in the world are experiencing the effects of climate change, so the goal of humanity is to achieve carbon neutrality. One of the main sources of CO2 emissions is the energy and construction sectors. However, renewable sources do not provide enough to cover energy consumption in many regions. Nuclear power is one possible solution, but it generates nuclear waste that needs to be stored safely.
The aim of this study is to investigate the diffusion process of gadolinium nitride solutions in light and heavy water in a novel recycled concrete made of red brick rubble; the Gd3+ ions are used to mimic diffusion of actinides. Diffusion dynamics is studied by the neutron imaging method. Due to the sensitivity of our neutron camera imaging system, we are the first who report also on direct imaging of the diffusion of heavy water through the concrete matrix. For the solutions used, the diffusion coefficients and diffusion rates are calculated by using the second Fick's law. The obtained results are valuable in terms of the search for a more sustainable and environmentally friendly option than convectional concrete in the construction of storage facilities for nuclear waste.
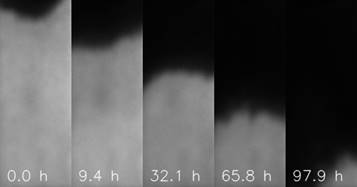
Figure 1: Neutron transmission images documenting the time evolution of diffusion
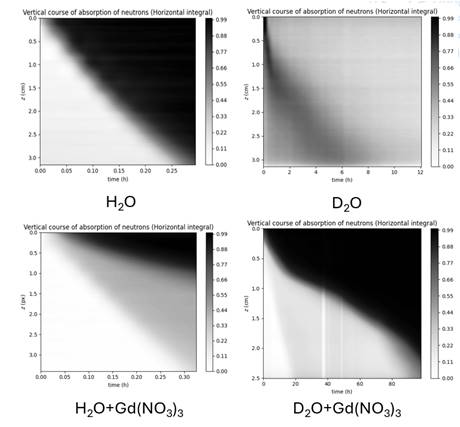
Figure 2: Time-Dependent Diffusion of Used Liquids in Concrete
.