Structure of halloysite nanotube with irinotecan solved by molecular simulation methods
M. Pospíšil1, M. Pšenička1, E. Gianni2 , D. Papoulis2, K. Avgoustakis3
1Charles University,
Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Prague, CZ
2Department of Geology, University of Patras, Rio, 26504, Patras,
Greece
3Department of
Pharmacy, University of Patras, Rio, 26504, Patras, Greece
miroslav.pospisil@mff.cuni.cz
Halloysite is a clay mineral derived from kaolinite with proven spiral-shape tubular crystal morphology and moreover biocompatible with the human body. It determines halloysite for possible use as drug delivery nanocarrier because it allows the encapsulation of various bioactive molecules. Halloysite nanotubes have been investigated as a potential drug delivery system of irinotecan for colon cancer treatment administered by the oral route [1]. To allow releasing of irinotecan in an intestinal environment the whole halloysite nanotubes loaded with irinotecan were coated with EudragitS100 to protect releasing of irinotecan in stomach pH. The loading efficiency of the halloysite nanotube for irinotecan was very high, reaching 84.42 ± 3.10 %. Experimental measurements like transmission electron microscopy showed that the irinotecan molecule is just on the surface of nanotubes and X-ray diffraction patterns proved that there was no intercalation of irinotecan among individual layers. Based on thermogravimetric analysis and tests with various weight ratios between halloysite and polymer was shown that drug release rate from the polymer-coated nanotubes was minimal (0.7 % in 2 h) at stomach pH (pH 1.2) and high at intestinal pH 7.4 conditions (when the pH was increased to 7.4, drug release increased by approx. 70 % in 2 h) [1]. Based on experimental results, methods of molecular simulations were used to determine mutual positions and arrangements of irinotecan molecules on the halloysite nanotube surface, which means the most probably structural model. Results of calculations showed that the most appropriate amount of irinotecan molecules for a given size of halloysite nanotube with a length of 25.359 Å is 6. This amount is in a good agreement with the molar weight ratio of the compounds determined from the real samples. Calculated models showed that the energetically preferred positions of the irinotecan molecules remain closed to the outer part of the halloysite nanotubes and longitudinal axes of irinotecan and the nanotube are parallel.
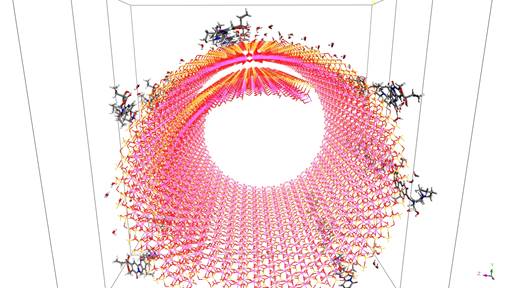
Figure 1. View along longitudinal axe for the optimized structure of the halloysite tube with 6 drug molecules.