On optimization of magnetic nanoparticles arrangement in
PS-b-P4VP block copolymer thin films
Alexander Zhigunov, Magdalena Konefał, Peter Černoch, Vitalii Patsula, Ewa Pavlova
Institute of
Macromolecular Chemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, Czech
Republic
zhigunov@imc.cas.cz
The arrangement of inorganic nanoparticles in
a polymer matrix or domains in block copolymer thin films has attached much
attention due to their potential applications in diverse fields such as block copolymer
lithography, nanostructured solar cells or advanced catalysts [1]. The key
issue in all of these systems, which is to precisely control the spatial
distribution of the nanoparticles, maintaining the thin film characteristics and
polymeric domain’s parameters, still remains a significant challenge [2].
In this work we demonstrate the effect of incorporating magnetite nanoparticles into polystyrene-poly-4-vinylpyridine (PS-b-P4VP) block copolymer thin films. The synthesized nanoparticles had a Fe3O4 core diameter of 7.2 nm and were coated by polyacrylic acid to improve affinity to P4VP block, giving overall hydrodynamic radius of 23 nm as measured by DLS. Solutions of the PS-b-P4VP were prepared in THF or THF/methanol mixture, where 2 wt. % of nanoparticles were mixed in. The films were prepared by dip-coating method with withdrawal speed varied in the range of 2 to 100 mm/min. The properties of the obtained films were characterized by the means of X-Ray Reflectivity, Grazing Incidence Small Angle X-ray Scattering, Atomic Force Microscopy and Transmission Electron Microscopy.
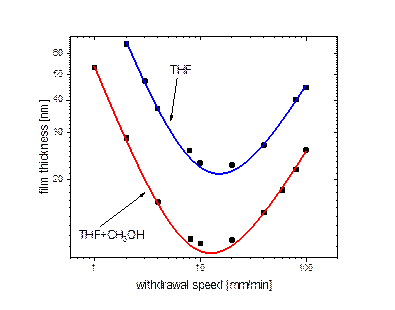
Figure 1. Film thickness as a function of the dip-coating rate. Red curve corresponds to the films, prepared from THF/methanol mixture; blue curve corresponds to the films, prepared from THF.
Thin films with thicknesses 9-70 nm were obtained. The V-shaped thickness dependence on withdrawal speed was validated for each system. For the films obtained from solvents mixture we have observed curve shift to lower dip-coating rates, but leading to possibility to achieve lower film thicknesses. Additionally, much better domain organization was obtained in the case of the films prepared from solvent mixture, especially in the capillarity regime (slow withdrawal speeds), while films prepared from THF solution showed an occurrence of particles aggregates on the surface. The addition of Fe3O4@PAA nanoparticles has been shown to induce the orientation of P4VP cylindrical nanodomains perpendicular to the surface. Domains of size in the range of 15 to 32 nm and spacing from 45 to 105 nm were obtained depending on the withdrawal speed. The optimal processing conditions have been found to fabricate long-range ordered hybrid organic-inorganic material without the need for further annealing or post-processing.
1. Park S. et al., Macromolecules 2007, 40, 22, 8119-8124
2. Gao K. et al., Langmuir, 2020, 36, 1, 194-203.
This
work was supported by Czech Science Foundation (GACR) (Grant no. 19-10982S).