CePt2Al2 - structural properties
Petr Doležal, Elen Duverger-Nedellec, Stanislav Daniš, Pavel Javorský
Faculty of Mathematics and
Physics, Charles University, Ke Karlovu
5, 121 16 Prague 2
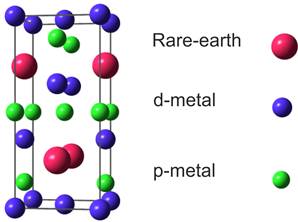
This work is focused on the structural and physical properties of CePt2Al2, an intermetallic compound. CePt2Al2 belongs to the Ce based 1:2:2 compounds, which crystalize in the structural model of CaBe2Ge2 type, see Fig.1 At low temperature this structure type becomes very often unstable and result in the structural phase transition from tetragonal to an orthorhombic structure as for example in CePd2Al2-xGax series.
CePt2Al2 is a new member of this family and behaves in different way. At room temperature the structure is orthorhombic and modulated as was determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction (Cmme(a00)000, with q⃗= (0.481, 0, 0)). The dependence of lattice parameters above room temperature was studied by X-ray powder diffraction showing the presence of structural transition to a tetragonal structure above room temperature, which could be presumably describe by CaBe2Ge2 structure type. This transition exhibits 50 °C hysteresis and creates a domain structure in the sample. During the transition both tetragonal and orthorhombic phases coexist and their ratio is dependent on cooling rate.
The investigation was also focused on specific heat, magnetization, and transport measurements in the temperature range between 0.5 and 300 K. Specific heat and magnetic susceptibility show an antiferromagnetic order below 2 K. Around 20 K the temperature dependence of electrical resistivity exhibits an upturn in typical metallic behaviour, which leads to the creation of local minimum. On the basis of electrical resistivity and other bulk measurements, CePt2Al2 can be considered a Kondo lattice material, for which the reduction of free magnetic Ce3+ moment is typical. The presence of a modulated crystal structure opens the possibility of a charge density wave state in CePt2Al2 as observed for (Re)Pt2Si2.