Structure Comparison of
Salivary Serpins from Ixodes ricinus
Barbora Kaščáková1, Tatyana Prudnikova 1, Jindřich Chmelař2 and Ivana Kutá Smatanová 1
1 Institute of
Chemistry, Faculty of Science, University of South Bohemia, Branišovská
1760, České Budějovice, Czech
Republic
2 Department of Medical
Biology, Faculty of Science, University of South Bohemia, Branišovská
1760, České Budějovice,
Czech Republic
barbora.karaffova@gmail.com
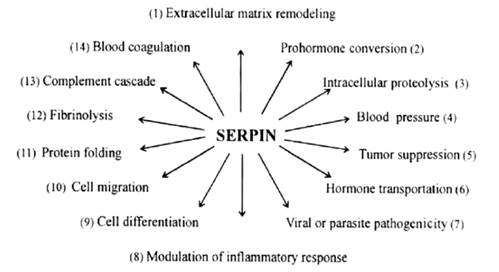
Serine protease
inhibitors-serpins is a group of ancient proteins widely distributed in nature
(3). Serpins function as serine protease inhibitors but during the evolution,
some serpins lost their inhibitory function and serve as molecular chaperones
(Heat shock serpin 47), tumor suppressors (Maspin), hormone transporters
(Cortisol-binding globulin) or as storage proteins (Ovalbumin) (1). Inhibitory
serpins vary in functions according to their specificity and their importance
is stressed by serpinopathies, diseases caused by serpin dysfunction or
deficiency. Many of today well-known diseases, such as emphysema, cirrhosis,
angioedema, hypertension and familial dementia, are associated at least
partially by serpin dysfunction (2). This makes serpins
interesting candidates for drug development and knowledge of detailed serpin
structure is necessary for it.