Isomeric forms of the organometallic-inorganic hybrid polymer [Cp*2Mo2P2Se3(CuI)3(CH3CN)]n
M. Dušek
Institute of Physics ASCR, v.v.i., Na Slovance 2, 18221 Praha 8, Czech Republic
dusek@fzu.cz
Recently, there was an article [1] published
about synthesis and characterization of a tripledecker
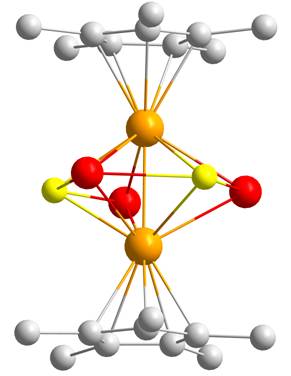
molecule [Cp*2Mo2P2Se3], Cp* = C5Me5),
and its use as a molecular building
block in the formation of copper(I) halide polymers. Reaction
of the tripledecker molecule (see Fig. 1) with copper(I) halides provides
polymers of diverse dimensionalities depending on competing coordination
properties of P and Se atoms.
The reaction of
the tripledecker molecule with CuI in CH3CN gave a mixture of
bright-red plates and dark prisms, both with a composition Cp*2Mo2P2Se3(CuI)3(CH3CN)]n,
in a temperature-dependent ratio. While structure of bright-red plates could be
solved by classical methods as a two-dimensional polymer, the structures of the
dark-red prisms was modulated. The modulation of tripledecker molecule is of harmonic
nature. On the other hand, discontinuous modulation function are needed for the
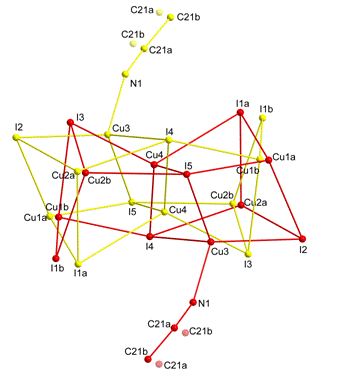
inorganic part whene a cage from Cu and I atoms (Fig. 2) alternates between two
positions. In three-dimensional description this lead to disorder, which is
resolved using crenel modulation function.
The presentation demonstrates way how to solve and refine this kind of structure. The steps with program Jana2006 [2] will be explained together with necessary underlying theory to the extent needed for understanding the presented procedures. Finally, still unsolved problems connected with solution of the title structure, will be discussed.
|
|
|
|
Figure 1. The tripledecker molecule. P yellow, Se red, Mo orange, C gray, hydrogen omitted. |
Figure 2. Two positions of the Cu-I cage observed as disorder in the average structure. |
1. M. Bodensteiner, M. Dusek, M.M. Kubicki, M. Pronold, M. Scheer, J. Wachter, M. Zabel, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2010, (2010), 5298.
2. V. Petricek, M. Dusek, L. Palatinus, Jana2006. The crystallographic computing system.
Institute of Physics, Praha, Czech Republic. http://jana.fzu.cz