Experience from Almelo Laboratory
Z. Matěj1*, J. F. Woitok2, A. Kharchenko2, R. Kužel1, V. Holý1
1Department of Condensed Matter Physics, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University in Prague, Ke Karlovu 5, 121 16 Praha 2, Czech Republic
2PANanalytical, Lelyweg 1, P.O. Box 13, 7600 AA Almelo, The Netherlands
e-mail*: matej@karlov.mff.cuni.cz
Samples:
Various types of x-ray optics in different diffraction geometries were tested on tree types of samples: a high quality epitaxial layer of GaMnAs, polycrystalline Cu samples prepared by severe plastic deformation and magnetron sputtered TiO2 nanocrystalline thin films. The aim of the project was to test selected x-ray optics modules and try to measure in nonconventional experimental arrangements as well as study structure of the samples.
Position sensitive detectors X'Celerator and PIXcel
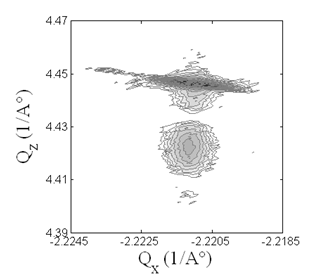
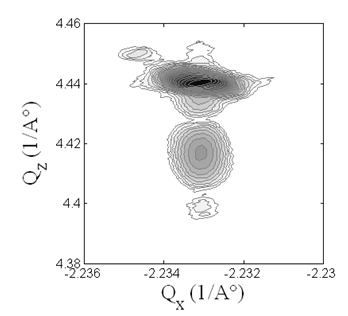
Both position sensitive detectors (PSDs) X’Celerator and a prototype of new detector PIXcel were available on an horizontal MRD system. The MRD system with the selected incidenc beam optics (a hybrid monochromator or a stand-alone mirror) was used mainly for high resolution experiments and parallel beam applications. Hence we utilized these detectors for reciprocal map measurements (Fig. 1 and 2) and for a measurement in the parallel beam geometry with a low take-off angle (Fig. 5).
|
|
|
|
Fig. 1: GaMnAs (204), Hybrid Monochromator, Triple axis analyzer, 15 h, note that the (204) is a weak diffraction for Zinc Blende type semiconductor structures |
Fig. 2: GaMnAs (204), Hybrid Monochromator, PIXcel, 2 h 20 min, 4x higher absolute intensity than with TA (Fig. 1) |
Comparison of Hybrid and a1 monochromators
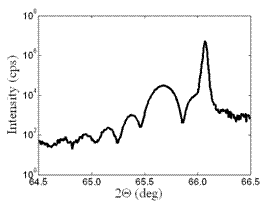
The 2X Hybrid Mirror/Monochromator was used for the high resolution measurements of the GaMnAs layer sample. The intensity gain was excellent with good angular resolution (Fig. 3). Only for higher diffraction angles ((006) diffraction) the broad spectral band-pass of the monochromater induced a significant broadening of the GaAs substrate peak.
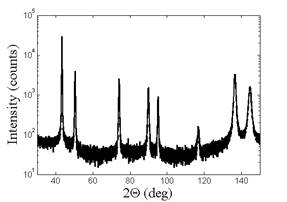
Both monochromators, the Hybrid and the Alpha1, were tested on polycrystalline Cu samples prepared by severe plastic deformation. The intensity of the focusing Alpha1 monochromator was very good, it was possible to utilize all advantages of the focusing symmetrical geometry (prog. slits, PSD detector). The shape of the peaks profiles was really nice (Fig. 4, potentially of enough quality to make possible evaluation of the dislocation density and arrangement). The intensity from the Cu sample measured by the 2X Hybrid Monochromator was lower. It is, however, necessary to consider that for this bulk polycrystalline sample the used parallel beam setup is not a good option. Just a very small part of the sample is irradiated in the symmetrical scan. It is not possible to use any PSD detector. On the other hand in comparison with the Bartels Monochromaters available in the MFF x-ray laboratory the intensity gain from the Hybrid Monochromator is much higher, hence also powder samples can be measured with excellent resolution.
Applications of the Alpha1 and the Hybrid Monochromators is well described in the X’Pert PRO User’s Guide.
|
|
|
|
Fig. 3: (004) diffraction of GaMnAs (50 nm), MPD, 2X Hybrid Monochromator, Mirror in the Diff. beam, 10 min |
Fig. 4: ECAP(1x) Cu sample, Alpha1 system, X’Celerator, 13 h |
Measurement of thin films - grazing incidence vs. grazing excidence
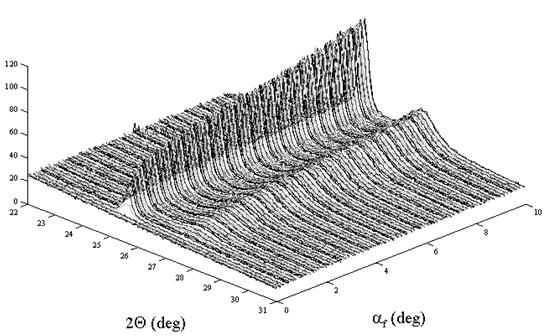
The aim of this experiment was mainly to check usefulness of a PSD detector in the parallel beam geometry for study of polycrystalline thin films. To achieve a good resolution instead of the 2Theta scan with a low incidence angle the experiment was done in the grazing exit geometry. The scan, a little bit unconventional in the Data Collector software, with a same step in the both angles, incident angle Omega as well as the diffracted angle 2Theta, was performed. The PSD detector was measuring spectra for some range of diffraction angles 2Theta for each step of the scan. Hence a series of 2Theta scans for different take-off angles Alphaf = 2Theta – Omega were acquired (Fig. 6). The exit angles were really low – close to zero. It should be possible to evaluate layer structure of the sample, however, it is complicated by texture.
|
|
|
Fig. 5: TiO2 thin film on Si substrate: Part of the measured spectra with the PSD in the low exit angle geometry. Anatase (101) – the higher peak at the lower 2Theta angle, Rutile (110) – the lower peak at the higher 2Theta angle; range of the exit angle: 0 – 10 deg. |