X-RAY STRUCTURE ANALYSIS OF DIHYDOERGOCRISTINE MESYLATES
H. Petříčková1a, M. Hušák1b, J.
Čejka1c, B. Kratochvíl1d, I. Císařová2,
A. Jegorov3
1Department of Solid State
Chemistry, Institute of Chemical Technology Prague, Technická 5, 166 28 Prague
6, Czech Republic, e-mail: apetrickh@vscht.cz,
bhusakm@vscht.cz, ccejkaj@vscht.cz, dkratochb@vscht.cz
2Department of Inorganic
Chemistry, Charles University, Hlavova 8, 128 43 Prague 2, Czech Republic,
e-mail: cisarova@natur.cuni.cz
3IVAX CR a.s., Research Unit,
Branišovská 31, 370 05 České Budějovice, Czech Republic, e-mail: alexandr_jegorov@ivax-cr.com
Dihydroergocristine
belongs to the dihydroergopeptine alkaloids [1].
These compounds are widely therapeutically used in medicine. Dihydroergocristine
exercises a double agonistic/antagonistic activity on dopaminergic and
adrenergic receptors, it also shows a non competitive antagonistic effect on
serotonine receptors. Dihydroergocristine protects the brain against the
metabolic effects of ischaemia by acting at a cellular level. It increases the
cerebral blood flow and the oxygen consumption of the brain [2]. A combination
of dihydroergocornine, dihydroergocristine and dihydroergokryptine (Hydergine)
is employed mainly in peripheral vascular disorders, hypertension, cervical
syndromes and in the interval treatment of migraine.
Four
new crystal structures of dihydroergocristine were determined by single crystal
diffraction, namely dh-ergocristine mesylate monohydrate bis(ethyl acetate)
solvate (1), dh- ergocristine
mesylate methanol solvate (2),
dh-ergocristine mesylate monohydrate bis(ethyl methyl ketone) solvate (3) and dh-ergocristine mesylate
monohydrate amyl acetate solvate (4).
CSD database contains only one crystal structure [3] of dihydroergocristine
mesylate (5).
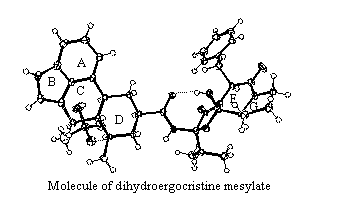 Conformation, molecular packing and also a system of hydrogen bonds in
crystal structures of 1, 2, 3,
4 and 5 were compared in detail. 1
and 4 crystallize in same structural
type and they are isostructural. Volume of the void 538 Ĺ3 in the
structure allows binding of even amyl acetate. Structures of 2 and 5 are also very related, but they are not isostructural. The third
structural type forms structure of 3.
Conformation, molecular packing and also a system of hydrogen bonds in
crystal structures of 1, 2, 3,
4 and 5 were compared in detail. 1
and 4 crystallize in same structural
type and they are isostructural. Volume of the void 538 Ĺ3 in the
structure allows binding of even amyl acetate. Structures of 2 and 5 are also very related, but they are not isostructural. The third
structural type forms structure of 3.
Conformations
of molecules of 1, 2, 3, 4
and 5 do not strongly differ. Rings A, B and E are planar. Ring C has
envelope conformation E3, ring D in all molecules of
dihydroergocristine possesses characteristic chair conformation 4C1,
ring F forms an envelope conformation 6E and the conformation of
proline ring G lies between 4T3
and 4T5.
Presence
of hydrogen bonds in the structures of dihydroergocristine mesylates is common.
One intramolecular O5-H…O1 and one intermolecular N2-H…O8 hydrogen bonds are characteristic
for all studied structures.
This work was
supported by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech
Republic (research project No. CEZ: MSM 223100002) and by the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (grants No. 203/00/D095, 203/99/0067, 203/99/M037,
203/01/0700).
1.
Z.Řeháček,
P. Sajdl: Ergot Alkaloids: Chemistry, Biological Effects, Biotechnology. Praha 1990.
Academia Praha,.
2. G. Coppi: Artzneimittelforschung 42(11A) (1992) 1381 – 1390.
3.
J.Čejka,
J.Ondráček, M.Hušák, B.Kratochvíl, A.Jegorov, J. Stuchlík: Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 60 (1995) 1333
– 1342.