Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of human cytomegalovirus UL144, an HVEM orthologue
M. Benko, A. Bitala, S. Lenhartová and I. Nemčovičová
Biomedical Research Center, Institute of Virology, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Bratislava, Slovakia
mario.benko@savba.sk
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is a β-herpesvirus that has co-evolved with the host immune system to establish lifelong persistence. HCMV within its unique long (UL)/b’ locus, encodes many immunomodulatory molecules, including the glycoprotein UL144 [1]. UL144 is a structural mimic of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member HVEM (TNFRSF14), which binds to the multiple cellular ligands, e.g, LIGHT, LTα, BTLA, CD160, and gD [2, 3]. UL144, while being an HVEM orthologue, binds exclusively only BTLA, avoiding activation of inflammatory signaling initiated by CD160 in natural killer cells. Although, BTLA and CD160 cross-compete for HVEM, the structural basis for the UL144 ligand selectivity remains unclear [3].
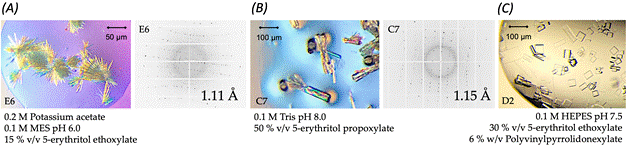
Figure 1. Crystals of HCMV UL144-DG (A-C) followed by X-ray diffraction images are shown. The crystals were obtained under above-mentioned crystallization conditions and tested for diffraction in DESY Hamburg.
The ectodomain of UL144 (wild-type, WT) contains a total of ten putative N-linked glycosylation sites. Many of them are not present in other viral species (e.g., Rhesus CMV UL144) suggesting interesting evolutionary consequences. However, due to high amounts of flexible N-linked glycans present in recombinant form of UL144-wt the glycosylation deficient mutant (UL144-DG) was generated and used for crystallization. Here, we report on UL144-DG crystallization by using standard vapor diffusion method. For the initial screening the high-throughput robotic system was set up with different commercial crystallization conditions (e.g., JCSG-plus, PACT premier or MIDAS plus). The protein solution of concentration > 3 mg/ml was mixed with precipitant in 1:1 or 2:1 ratio. The crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction measurement were observed in precipitant conditions containing 5-erythritol propoxylate or ethoxylate. Diffraction data were collected at macromolecular crystallography beamline P13 at DESY (Hamburg). The most promising UL144-DG crystals diffracted to 1.1 Å resolution.
1. T. L. Murphy, and K. M. Murphy, Annu Rev Immunol 28, (2010), 389–411.
2. C. F. Ware CF, and J. R. Šedý, Curr Opin Immunol 23, (2011), 627-31.
3. J. R. Šedý, and M. O. Balmert et al., J Biol Chem 51, (2017), 21060–21070.
This research was funded by the contribution of the Slovak Research and Development Agency under the project APVV-19-0376 and the contribution of the Scientific Grant Agency of the Slovak Republic under the grant VEGA-02/0026/22.