Structural Interpretation of J-coupling Constants Calculated in Guanosine and Deoxy-Guanosine: Influence of Sugar-Phosphate-like Backbone Conformation, Sugar Pucker and Solvent Environment
Zuzana Vokáčová1,2, F. Matthias
Bickelhaupt3, Jiří Šponer4 and Vladimír Sychrovský1
1Institute
of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry, v.v.i.,
The relationship between the
the glycosidic torsion angle c,
the three-bond couplings 3J(C8-H1’) and 3J(C4-H1’), and
the four one-bond couplings 1J(C8-H8), 1J(C1’-H1’), 1J(C2’-H2’)
and 1J(C2’-H2’2) in deoxyguanosine and the three one-bond couplings 1J(C8-H8),
1J(C1’-H1’) and 1J(C2’-H2’) for guanosine has been
analyzed using density functional theory - B3LYP /6-31G**. The influence of the
backbone conformation, sugar composition and the sugar pucker, and molecular
environment including water solvation has been also considered.
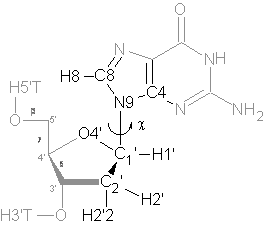
Figure 1: Numbering of atoms and definition of torsion angles in deoxy-Guanosine.
Acknowledgements: This work was
supported by the Grant Agency of the Czech Academy of (grants no.
IAA400550701), by the