MACE-Interactive: A Browser-Based GUI for Atomistic Simulations with MACE Foundation Models
J. Drahokoupil1,3, M. Lebeda1,2,3
1 Institute of Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Na Slovance 2, 18200 Prague 8, Czech Republic
2 Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague, Trojanova 339/13, 12000 Prague 2, Czech Republic
3 Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague, Technická 4, 16607 Prague 6, Czech Republic
lebedmi2@cvut.cz
Pre-trained foundation models in machine-learning interatomic potentials (MLIPs) allow researchers to perform accurate and efficient atomistic simulations without the need to search for or fit a potential for each studied system. These universal models approach the accuracy of density functional theory (DFT) while being orders of magnitude faster, making it feasible to study systems with even more than thousands of atoms, well beyond the practical size limits of DFT.
We have developed MACE-Interactive, a browser-based graphical interface designed to streamline calculations with the MACE MLIP foundation models [1]. The application supports multiple simultaneous structure uploads (POSCAR, CIF, LMP, XYZ with lattice), and presents calculated results in an easily readable way, allowing direct comparison between structures. Currently, the MACE-Interactive provides single-point energies, geometry optimizations, elastic properties, and phonon calculations, as well as genetic algorithm for identifying the energetically most favourable arrangements of substitutions or vacancies. The tool can also generate fully configured Python scripts based on the parameters set by the user in the interface for external console execution. The source code and installation instructions are provided at github.com/bracerino/mace-md-gui, with a video tutorial illustrating the application use and capabilities at: https://youtu.be/xh98fQqKXaI.
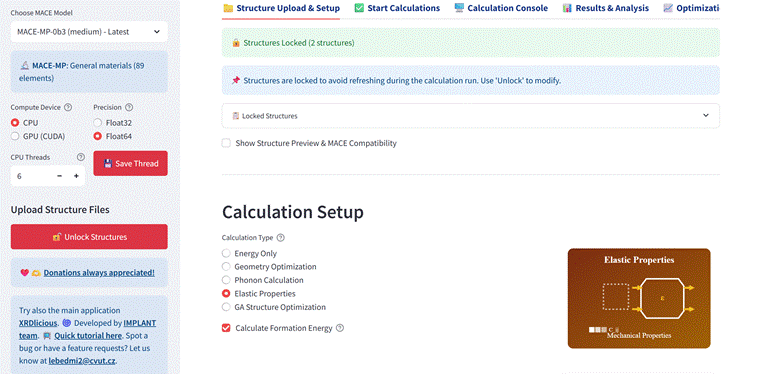
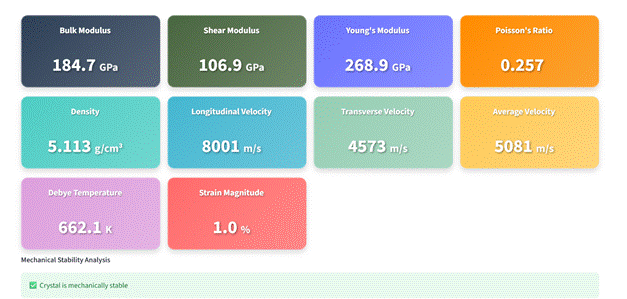
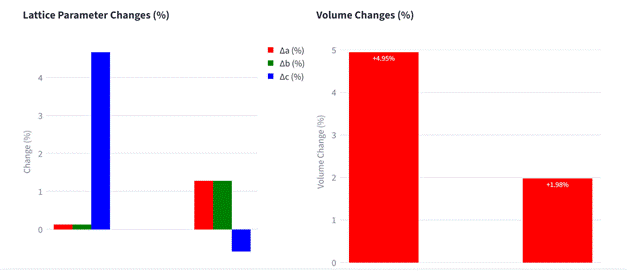
Figure 1. Example of MACE-Interactive: Calculation setup, computed elastic properties, and differences in lattice parameters before and after geometry optimization.