Crystallization of the MET extracellular domain with crystallization chaperones
T. Meyer, H. H. Niemann
Structural Biochemistry, Department of Chemistry, Bielefeld University, Universitätsstraße 25, 33615 Bielefeld, Germany
timo.meyer@uni-bielefeld.de
The human receptor tyrosine kinase MET is activated upon binding of the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), its endogenous ligand. MET-activation plays an essential role in development and wound healing and induces diverse responses in several cell types, such as proliferation, motility, morphogenesis and angiogenesis. The structure of the complete dimerized MET ectodomain together with HGF is still unknown. The MET ectodomain consists of the six subdomains SEMA, PSI, and the Ig-like domains Ig1, Ig2, Ig3 and Ig4. While a rigid-body model could be calculated from SAS data [1], the crystallization of MET constructs containing Ig2, Ig3 and Ig4 still remains challenging, most likely due to high interdomain flexibility.
A promising approach to overcome this issue and solve the structure of MET is the use of interaction partners as crystallization chaperones. This technique was initially successfully applied for the MET SEMA-domain together with the HGF β-chain [2]. Moreover, the pathogenic bacterium Listeria monocytogenes also binds to MET via its surface protein InternalinB (InlB), essentially hijacking the MET signalling pathway and inducing the uptake of Listeria into otherwise nonphagocytic cells. Recombinant InlB could be utilized to stabilize the SEMA-, PSI- and Ig1-domain for crystallographic analyses [3, 4].
In our most recent studies, we focused on this approach and were able to obtain a more defined structure of the Ig2 domain. In addition, we identified a wider set of MET binding proteins for further crystallization trials to finally solve the structure of the whole MET extracellular domain.
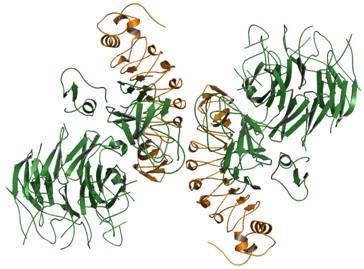
Figure 1. MET741 (green) together with InlB321 (orange).
1. H. H. Niemann, M. V. Petoukhov, M. Härtlein, M. Moulin, E. Gherardi, P. Timmins, D. W. Heinz, D. I. Svergun, J. Mol. Biol., 377, (2008), 489–500.
2. J. Stamos, R. A. Lazarus, X. Yao, D. Kirchhofer, C. Wiesmann, The EMBO Journal, 23, (2004), 2325–2335.
3. H. H. Niemann, V. Jäger, P. J. G. Butler, J. van den Heuvel, S. Schmidt, D. Ferraris, E. Gherardi, D. W. Heinz, Cell, 130, (2007), 235–246.
4. D. M. Ferraris, E. Gherardi, Y. Di, D. W. Heinz, H. H. Niemann, J. Mol. Biol., 395, (2010), 522–532.