Structural insides into substrate tunnels of bacterial lipoxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Jacqueline Kalms1, Swathi Banthiya2, Hartmut Kuhn2 and Patrick Scheerer1,*
Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin , Charitéplatz 1, D-10117 Berlin, Germany
1Institut für Medizinische Physik und Biophysik (CC2) - Group Protein X-ray Crystallography and Signal Transduction, 2Institut für Biochemie (CC2)
*patrick.scheerer@charite.de
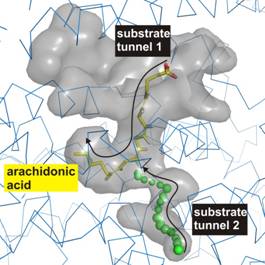
Lipoxygenases are non-heme iron containing enzymes catalyzing the dioxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids [1, 2]. The reaction specificity of these enzymes has been used as parameter for their classification. Lipoxygenase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA_LOX) oxygenates the substrates arachidonic acid and linoleic acid [3, 4]. After hydrogen abstraction at the active site and rearrangement of a radical, a second substrate, molecular dioxygen, inserts stereospecific, forming a hydroperoxy fatty acid. To make the lipoxygenase reaction possible at the deeply buried active site tunnels for both substrates from the protein surface to the catalytic centre are needed. Two crystal structures of PA_LOX show an active site bound endogenous lipid ligand in a tunnel [4]. To determine the hydrophobic tunnel for molecular dioxygen calculations with the program Caver were examined [5]. We found a second tunnel opening leading to the centre of catalysis. Dockings of the substrates arachidonic acid and linoleic acid show the hydrogen involved in the hydrogen abstraction as well as the accessibility to the carbon for oxygen insertion [6].
1. Haeggstrom, J. Z., and Funk, C. D. (2011) Lipoxygenase and leukotriene pathways: biochemistry, biology, and roles in disease. Chemical reviews 111, 5866-5898.
2. Kuhn, H., Banthiya, S., and van Leyen, K. (2015) Mammalian lipoxygenases and their biological relevance. BBA 1851, 308-330.
3. Garreta, A., Val-Moraes, S. P., Garcia-Fernandez, Q., Busquets, M., Juan, C., Oliver, A., Ortiz, A., Gaffney, B. J., Fita, I., Manresa, A., and Carpena, X. (2013) Structure and interactionwith phospholipids of a prokaryotic lipoxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FASEB journal 27, 4811-4821.
4. Banthiya, S.*, Kalms, J.*, Yoga E. G., Ivanov, I., Carpena, X., Hamberg, M., Kuhn, H., and Scheerer, P. (2016) Structural and functional basis of phospholipid oxygenase activity of bacterial lipoxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, submitted.
5. . (2012) CAVER 3.0: A Tool for the Analysis of Transport Pathways in Dynamic Protein Structures. PLoS Computational Biology 8: e1002708, 8(10).
6. Kalms, J.*, Banthiya, S.*, , Yoga E. G.*, Ivanov, I., Carpena, X., Kuhn, H., and Scheerer, P. (2016) The crystal structure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipoxygenase Ala420Gly mutant explains its altered reaction specificity, in preparation