Zr derivatives of di- and tetra- phosphonic acids: structural
variability studied by X-Ray
powder diffraction data
Ferdinando Costantino,
Riccardo Vivani
Dipartimento di Chimica, Via Elce di Sotto 8, 06123 Perugia, Italy
The recent
metodologies developed for structural determination from X-ray powder
diffraction, allowed us to solve the structures of many Zr phosphonates
prepared in our laboratory.
Metal
phosphonate based materials are today widely investigated from a fundamental
point of view and also for their potential application in molecular and ionic
recognition, catalysis, and solid state proton conductivity.
Reaction of
zirconium (IV) fluorocomplexes with R-amino-N,N-bis methylphosphonic and
diamino-N, N, N’, N’ - tetraphosphonic acids led to the formation of insoluble
microcristalline solids with a great structural variability; solids with
different connectivity and dimensionality were obtained by varying the nature
of R groups, using different building blocks.
Common
structural features in all the these solids were found, such as non-covalent
interactions that played a crucial role in the connectivity, acting as
“structure orienting factors”.
A class of
structures of new Zr phosphonates solved “ab-initio” using conventional powder
diffractometer will be presented, and the application of different methods for
structure solution will be also discussed.
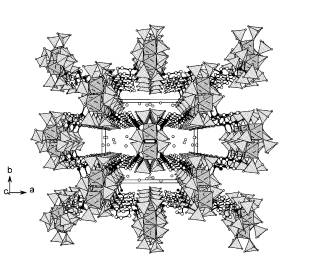
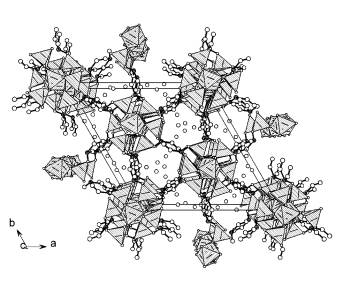
Fig.1 Structure of Zr
1,4-diaminocyclohexyl Fig.2
Structure of Zr 1,4-piperazine diphosphonate
tetraphosphonate
1) G. Alberti, M. Casciola, U. Costantino, R. Vivani, Adv. Mater., 1996,8,291
2) G. Alberti, in Comprehensive Supramolecular Chemistry, ed G. Alberti and T. Bein, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1996, vol 7, Chap.5.
3) U. Costantino, M. Nocchetti , R. Vivani, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002,124,8428.