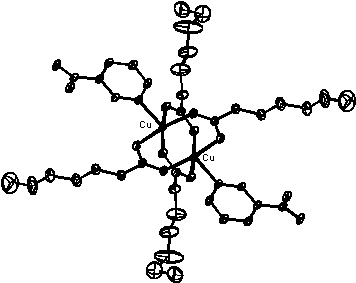
STRUCTURE OF TETRAKIS(HEPTANOATO)- BIS(NICOTINAMIDE)DICOPPER(II)
Nina
Petrovcic, Bojan Kozlevcar, Ivan Leban, Primoz Šegedin1
and Gerald Giester2
1Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical Technology, University of Ljubljana, Aškerèeva 5, P.O.B. 537, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia; e-mail: nina.petrovcic@uni-lj.si
2Universität
Wien, Geozentrum, Institut für Mineralogie und Kristallographie,
Althanstraße 14, A-1090 Wien, Austria
Carboxylic acid complexes of copper(II) are of special chemical and biological interest . Different pharmacological effects have been established in this type of compounds suggesting fungicidal and insecticidal activity. The structure analysis confirmed the expected dimeric form. Four bidentate heptanoate anions form bridges between copper atoms which have an effective 4+1 environment. The coordination around copper atom is made up of four O atoms of heptanoate groups in the basal plane, the apical positions being occupied by the N atoms of nicotinamide moieties. The Cu...Cu distance of 2.612(3) Å is typical for dimeric Cu complexes. As expected there is a considerable thermal motion at the terminal C atoms of the heptanoate residues.
CRYSTAL DATA
C40H64Cu2N4O10, Mr= 888.03 gmol-1, monoclinic, C2/c, lMoKa= 0.71073 Å , Nonius KappaCCD area detector; a= 23.193(5), b= 9.886(2), c= 20.942(4) Å , ß=99.68(3)o, V= 4733.3 Å 3, Z= 4, Dcalc=1.247 gcm-3; green crystals, current R1= 0.044 for 3189 reflections with I > 4s(I), wR2 = 0.141 for all 4772 data, refinement on F2, 262 parameters (SHELX97, PLATON98). Work on the polymorphic form in P21/c is in progress.
The financial support of The Ministry of Science and Technology, Republic of Slovenia, through grant J1-7313-103 is gratefully acknowledged.
