 |
 |
 |
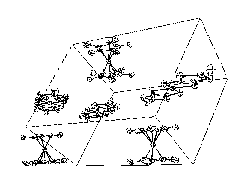
| Fig.1- Packing of 1 [Fe(Cp*)2][Pt(dmit)2] |
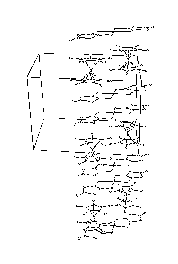
Fig.2- Packing of 2
[Fe(Cp*)2][Pd(dmio)2] |
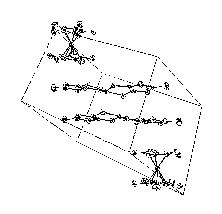
Fig.3- Packing of 3 Fe(Cp*)2][Ni(dsit)2] |
STRUCTURAL AND MAGNETIC CHARACTERISATION OF [Fe(Cp*)2]+ SALTS OF Pt(dmit)2, Pd(dmio)2 and Ni(dsit)2 ANIONS
S. Rabaça1; V. Gama1; D. Belo1; I.C. Santos1 ; M.T. Duarte2
1 Instituto Tecnológico e Nuclear,
P-2686 Sacavém (Portugal)
2 Instituto
Superior Técnico, P-1096 Lisboa (Portugal) E-mail: sandrar@itn1.itn.pt
Keywords: molecular magnetic materials, crystal
structure, metal dicahalcogenates
The crystal structures and magnetic properties of [Fe(Cp*)2][Pt(dmit)2] (1), [Fe(Cp*)2][Pd(dmio)2] (2) and [Fe(Cp*)2][Ni(dsit)2] (3) are presented and discussed. L = dmit (2-thiona-1,3-dithiol-4,5-dithiolate), dmio (2-oxo-1,3-dithiol-4,5-dithiolate) and dsit (2-thiona-1,3-dithiol-4,5-diselenate).
In this series of compounds essentially two types of structures where observed: one (I) consisting on 1D ..DDAADDAA.. stacks with side by side pairs of cations alternating with face to face pairs of anions, as in the case of [Fe(Cp*)2][Ni(dmit)2]1, and another (II) consisting of 2D layers composed of ..DDADDA.. stacks separated by sheets of acceptor anions, neutralising the charge, as in the case of [Fe(Cp*)2][Ni(dmio)2]MeCN2.
In this family of compounds, [Fe(Cp*)2][M(L)2], where M = Ni, Pd and Pt and L = dmit, dmio and dsit, the magnetic behaviour can be dominated either by ferromagnetic interactions, as in [Fe(Cp*)2][Ni(dmit)2]1 and [Fe(Cp*)2][Ni(dmio)2]MeCN2, or by antiferromagnetic interactions, as for 1, 2 and 3.
The nature of the magnetic interactions depends on the metallic element from the dithiolate complex and on the crystal structure, and it is essentially due to the interactions between the dichalcogelenes acceptor complexes. The compounds 1, 2 and 3 present a type I crystal structure, and the dichalcogenide acceptors are dimerized through Pt-S, Pd-Pd and S-S contacts respectively.
At room temperature the effective magnetic moment are 2.9, 2.7 and 3.1 B for 1, 2 and 3 respectively, while the calculated value for a non interacting system is 3.15 B. The obtained values indicate that the AFM exchange coupling is rather weak for 3 and somewhat stronger in the case of 1 than in 2.
Compounds crystallise
respectively in:
1: Triclinic P-1, a = 9.997(1)A, b= 11.554(1)A, c = 15.108(2)A; =109.72(1)o, =97.62(1)o, = 93.78(1)o
2: Triclinic P-1, a = 14.133(2)A, b= 14.620(2)A, c = 16.055(2)A; = 88.44(1)o, =80.25(1)o, =86.38(1)o
3: Triclinic P-1, a =
9.650(1)A, b= 11.439(2)A, c = 16.643(2)A; =71.14(1)o, =73.24(1)o,=89.72(1)o
Figures 1, 2, 3 show the packing
obtained in the crystal structures of the different compounds.
 |
 |
 |
| Fig.1- Packing of 1 [Fe(Cp*)2][Pt(dmit)2] |
Fig.2- Packing of 2
[Fe(Cp*)2][Pd(dmio)2] |
Fig.3- Packing of 3 Fe(Cp*)2][Ni(dsit)2] |