Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
POLYOXOMETALATES CONTAINING COORDINATIVELY BOUND ORGANIC LIGANDS
Neven Strukan, Marina Cindric', Maja Devčic' and Boris Kamenar
Laboratory of General and Inorganic
Chemistry, Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, University of Zagreb, Ulica kralja
Zvonimira 8, HR-10000 Zagreb, Croatia
e-mail: bkamenar@public.srce.hr
Keywords: crystal structure,
polyoxometalates, molybdovanadates, oxalate, glycine.
There is a considerable interest in the chemistry of
polyoxometalates with simple organic subunits (such as carboxyl, carbonyl, alkoxy and
organonitrogen groups) due to their importance as models for the interactions between
catalytic metal oxide surface and organic molecules. As part of our research four novel
polyoxomolybdovanadates have been prepared and their structures determined by
X-ray diffraction. Their crystal data are:
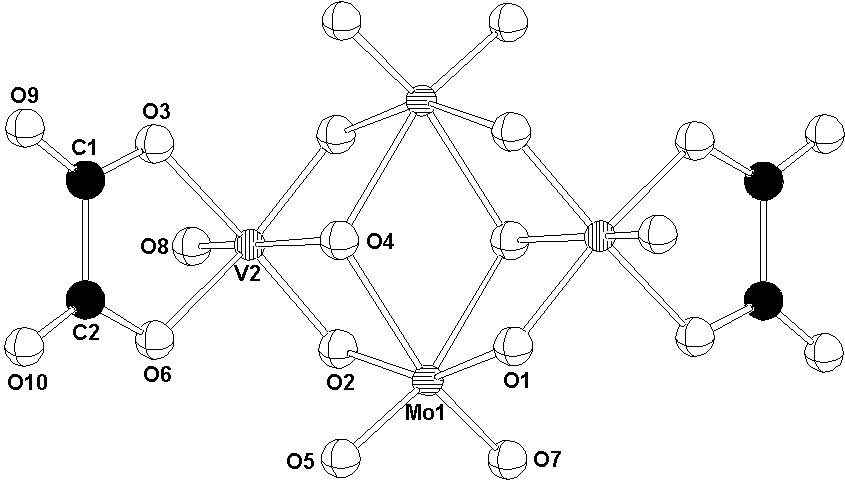
The centrosymmetric [H2Mo2V2O12(C2O4)2]4- anion of (I) is built up of two MoO6 and two VO6 edge-sharing octahedra, with bidentate oxalato ligands bonded to the vanadium atoms (Fig. 1).
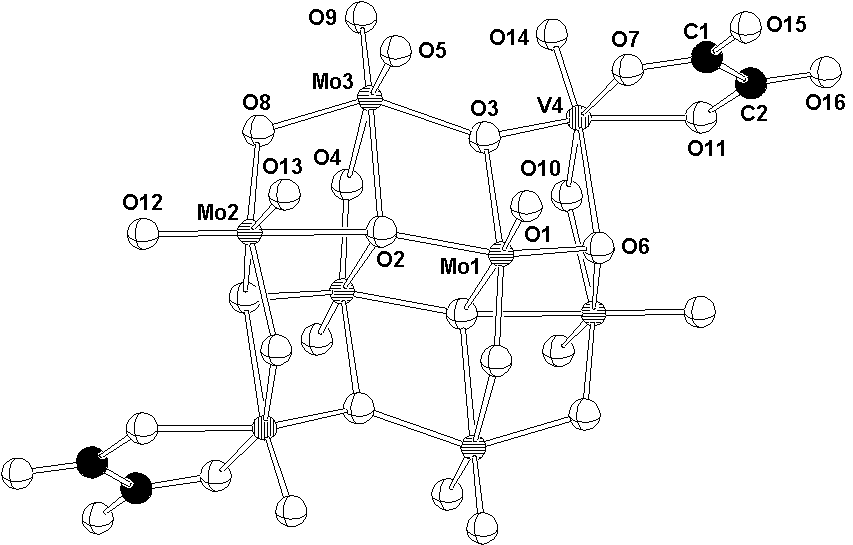
The molybdovanadate anion [Mo6V2O24(C2O4)2]6- found in (II) and (III) consists of six MoO6 and two VO6 edge-sharing octahedra, and adopts -[Mo8O26]4- type structure (Fig. 2). Bidentate oxalato ligands are also linked to the vanadium atoms.
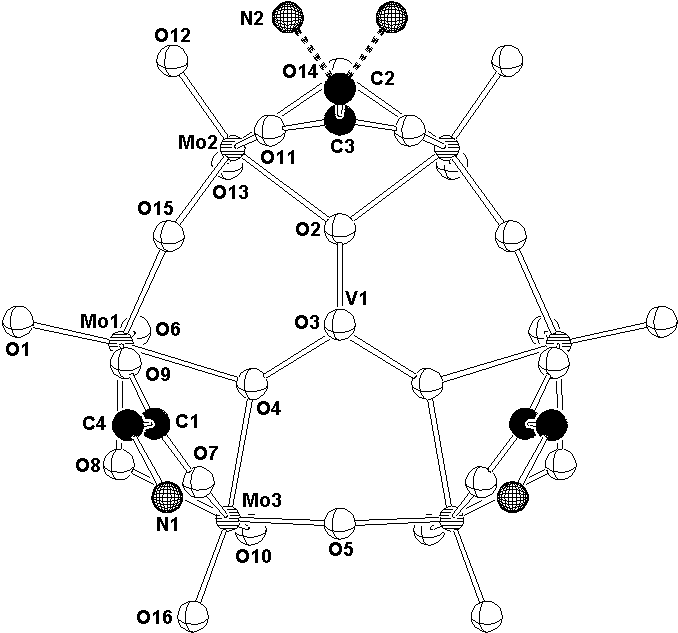
In (IV) polyanion [HMo6VO22(NH3CH2COO)3]2-
with a mirror plane symmetry is built up of six MoO6 edge-sharing octahedra
connected into a ring centred by VO4 tetrahedron. The MoO6 octahedra
are in pairs linked by the bridging glycine-carboxylato ligands (Fig. 3). To keep the
compound electrically neutral one hydrogen atom must be attached to the anion. Its
position was located in a difference map.
 |
 |
 |
Fig. 1 |
Fig. 2 |
Fig. 3 |
Figure 1. Figure 2.
Figure 3.