AROMATICITY OF FIVE-MEMBERED HETEROCYCLES. APPLICATION OF THE HOMA INDEX TO 1,2,4-TRIAZOLES
Agnieszka Mrozek, Janina Karolak Wojciechowska,
Institute of General Chemistry, Technical University of Lód, 90-924 Lód, Poland
Five-membered heteroaromatic rings often appear in compounds of biological activity. Numerous derivatives of piroles, furanes, thiofenes or imidazoles are included in both- animal and plant organisms as component of aminoacids and proteins [1]. Our interest in heterocyclic compounds is a result of previous investigations on thiadiazole and acridine derivatives [2,3].
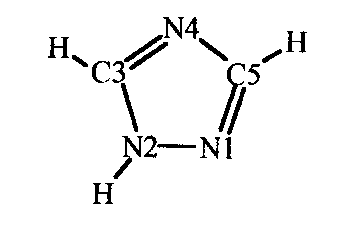
Principal goal of our recent investigation is to find correlation between kind and number of ring's substituents and heteroring aromaticity. Reinterpretation of theoretical basis of aromaticity and modification of aromaticity indexes, previously formulated only for carbon rings, let us apply them to heterorings. We have adapted to our work HOMA index (4) as a quantitative measure of aromaticity, classified as structural one. Firstly we use triazoles as model molecules (Fig l.)

Figure l. Molecule of 1,2,4- triazole
Review of CSD (CSD, version of November 1997 with 170000 entries in the connectivity file) gave us 222 compounds containing 1,2,4-triazole ring. For all objects, HOMA index calculations were done.
Simultaneously structure of 2-amino-5-[2'-diethylamino)ethylthio)-1,3,4-triazole hydrochlo- ride were determined and structure description will be enclosed. As a result of our investigation we confirm that: